Certain property does not qualify for the section 179 deduction. You placed both machines in service in the same year you bought them. They do not qualify as section 179 property because you and your father are related persons. You cannot claim a section 179 deduction for the cost of these machines.
- As of December 31, 2022, the depreciation allowed or allowable for the three machines at the New Jersey plant is $23,400.
- You deduct 80% of the cost ($360,000) as a special depreciation allowance for 2023.
- Land improvements include swimming pools, paved parking areas, wharves, docks, bridges, and fences.
- Assume the same facts as in Example 1 under Property Placed in Service in a Short Tax Year, earlier.
- You do not use the item of listed property predominantly for qualified business use.
Declining Balance Depreciation Calculator
Let’s assume that FitBuilders, a fictitious construction company, purchased a fixed asset worth $12,500 on Jan. 1, 2022. The company estimates that its useful life will be five years and its salvage value at the end of its useful life would be $1,250. The declining balance method formula shown below is used to calculate the declining balance rate (DB Rate). It is determined by estimating the number of units that can be produced before the property is worn out. The established amount for optional use in determining a tax deduction for automobiles instead of deducting depreciation and actual operating expenses.
What Is the Declining Balance Method of Assets Depreciation?
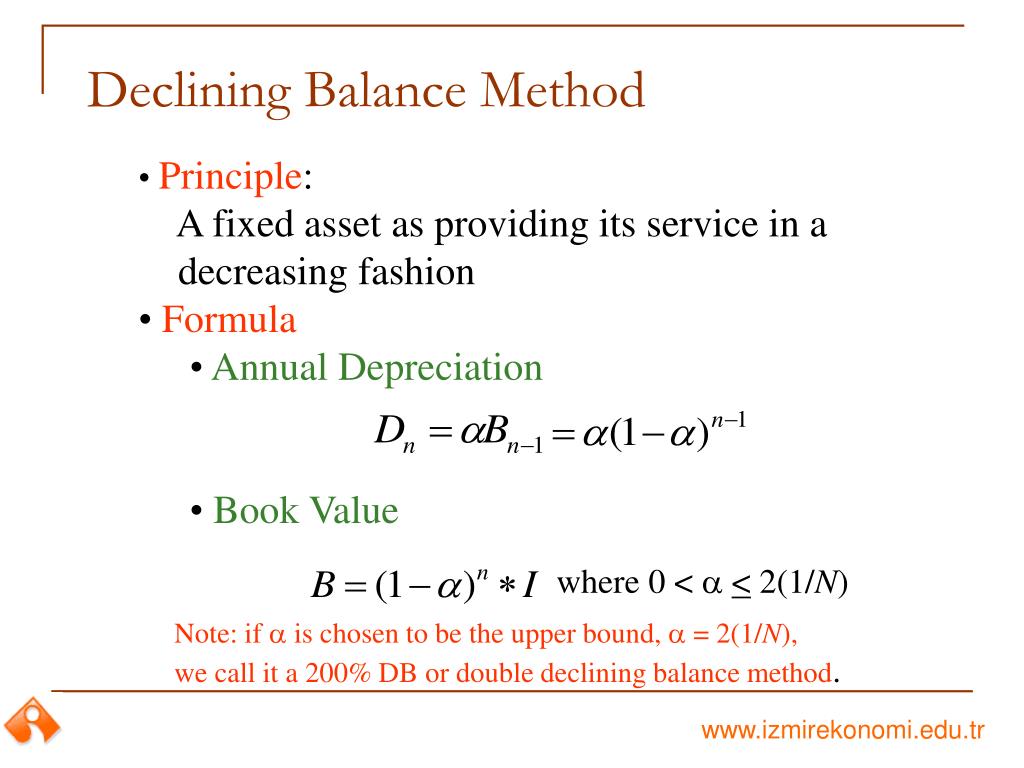
The company can calculate declining balance depreciation for fixed assets with the formula of the net book value of fixed assets multiplying with the depreciation rate. Choosing the right method of depreciation to allocate the cost of an asset is an important decision that a company’s management has to undertake. Companies need to opt for the right depreciation method, considering the asset in question, its intended use, and the impact of technological changes on the asset and its utility.

Double-Declining Balance Depreciation Method
The MACRS method for short-lived assets uses the double declining balance method but shifts to the straight line (S/L) method once S/L depreciation is higher than DDB depreciation for the remaining life. Meanwhile, long-lived assets use the straight line method for MACRS. In May 2017, you bought and placed in service a car costing $31,500.
Understanding Methods and Assumptions of Depreciation
Under the income forecast method, each year’s depreciation deduction is equal to the cost of the property, multiplied by a fraction. For more information, see section 167(g) of the Internal Revenue Code. You figure your share of the cooperative housing corporation’s depreciation to be $30,000. Your adjusted basis in the stock of the corporation is $50,000.
Calculate declining balance depreciation
Since the assets will be used throughout the year, there is no need to reduce the depreciation expense, which is why we use a time factor of 1 in the depreciation schedule (see example below). We can incorporate this adjustment using the time factor, which is the number of months the asset is available in an accounting period divided by 12. The following section explains the step-by-step process for calculating the depreciation expense in the first year, mid-years, and the asset’s final year. This is because, unlike the straight-line method, the depreciation expense under the double-declining method is not charged evenly over the asset’s useful life. In this lesson, I explain what this method is, how you can calculate the rate of double-declining depreciation, and the easiest way to calculate the depreciation expense.
For a discussion of business/investment use, see Partial business or investment use under Property Used in Your Business or Income-Producing Activity in chapter why choose a career in accounting 1. Reduce that amount by any credits and deductions allocable to the property. The following are examples of some credits and deductions that reduce basis.
If you made this election, continue to use the same method and recovery period for that property. On July 1, 2023, you placed in service in your business qualified property (that is not long production period property or certain aircraft) that cost $450,000 and that you acquired after September 27, 2017. You deduct 80% of the cost ($360,000) as a special depreciation allowance for 2023. You use the remaining cost of the property to figure a regular MACRS depreciation deduction for your property for 2023 and later years. Dean does not have to include section 179 partnership costs to figure any reduction in the dollar limit, so the total section 179 costs for the year are not more than $2,890,000 and the dollar limit is not reduced.
The company usually does this to prevent charging depreciation on the fixed asset forever as the net book value in the formula of declining balance depreciation above will reduce bit by bit as time passes but it will not become zero. As the declining balance depreciation uses the net book value in the calculation, the company doesn’t need to determine the depreciable cost like other depreciation methods. In other words, unlike other depreciation methods, the salvage value is ignored completely when the company calculates the declining balance depreciation. However, when the depreciation rate is determined this way, the method is usually called the double-declining balance depreciation method. Though, the double-declining balance depreciation is still the declining balance depreciation method.
